Welcome to the Internet Alerts – Routing API Quick-Start Guide! This guide is meant to be a non-programming look at Dyn’s Internet Alerts – Routing API and will cover the conceptual steps needed to use the API.
Organizing your Networks
Internet Alerts – Routing API is organized around your personal portfolio of network assets and inventories of those assets. An asset is a network prefix, like 204.13.248.0/22, or an ASN (autonomous system number), like 33517. (Assets can also be IP addresses or domain names, but those aren’t used for routing alarms.)
To enable monitoring, you first create an inventory in your portfolio, then add assets — prefixes and ASNs — to monitor. You can configure assets in bulk by uploading a file of prefixes and/or ASNs.
Monitoring is enabled or disabled per inventory, so that sets of networks can have their monitoring turned off for periods of anticipated operational management.
Inventories can be used to reflect a user’s geographic or logical organization of their networks, e.g. ‘IT Infrastructure’, ‘Dependent services’.
Internet Alerts – Routing API is designed to be called programmatically and the examples here are all shown using standard cURL commands. Authentication is achieved by passing in your username and password credentials using HTTP basic auth.
Portfolio Hierarchy
Assets (prefixes or ASNs) are organized into inventories. Your portfolio inventories can reflect your physical network, your logical network, or any other organizational method that works for you.
This graphic (Figure 1) shows the outline of a portfolio with several inventories and assets in each inventory. Each user account has one portfolio. The portfolio can contain multiple inventories. Each inventory contains one or more assets (prefixes or ASNs). Each asset (prefix or ASN) can belong to one or more inventories.
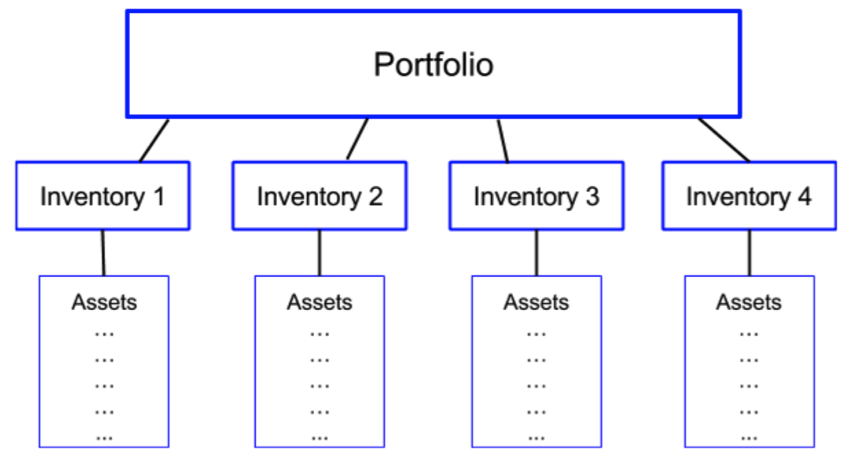
Figure 1
Create A Routing Alerts API Users and API Key
Follow these instructions to create API users and keys for your account. If you do not have a DynID (portal.dynect.net logon credentials), use the authentication method below.
Authentication
The API uses HTTPS with Basic Authentication, so make sure that your HTTP client library or tool supports basic auth.
For example, this document uses the cURL command-line tool, which supports basic auth using -u:
curl -u 'you@example.com:yourpassword' ...
where you@example.com is your DII username.
In the rest of this document, we’ll use username:password as the login credentials.
Response Status Codes
The following status codes will be used in responses from calls to the API:
| Status Code | Definition | Meaning |
| 200 | OK | Successful API call. Seen when requesting a list of assets or alerts, for example. |
| 201 | CREATED | The asset or an inventory was successfully added to the portfolio. |
| 204 | NO CONTENT | The asset or inventory was deleted.The object was modified. The object can be a monitoring option, or suppressing or acknowledging alerts.
The term “No Content” refers to the information that is passed back after a request is made. The request is completed, but there is no response content. |
| 400 | BAD REQUEST | The API call is not created properly. Check your API call, correct, and resubmit. |
| 403 | FORBIDDEN | User does not have permission to make the API request. |
| 500 | INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Please contact Dyn’s support. |
